Linux系统定制
适用范围
Ubuntu18.04 对于其他 Ubuntu 的版本,可供参考。
1.修改rootfs分区
若需要rootfs分区更大, 则需要把其它分区删除以便有空余的空间, 比如userdata分区的空间。
1.1.查看整个eMMC分区情况
fdisk -l /dev/mmcblk0
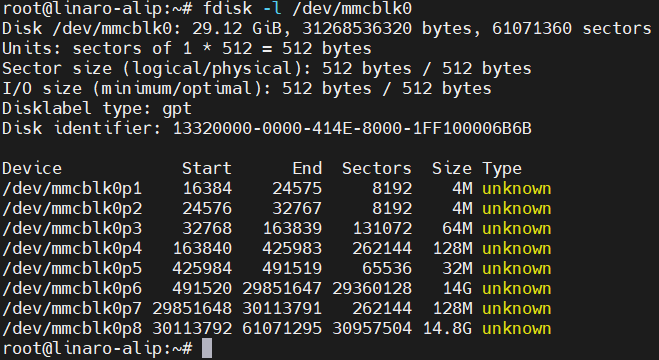
1.2.卸载已挂载的分区userdata及oem分区
umount /userdata
umount /oem
1.3.删除userdata及oem分区
fdisk /dev/mmcblk0
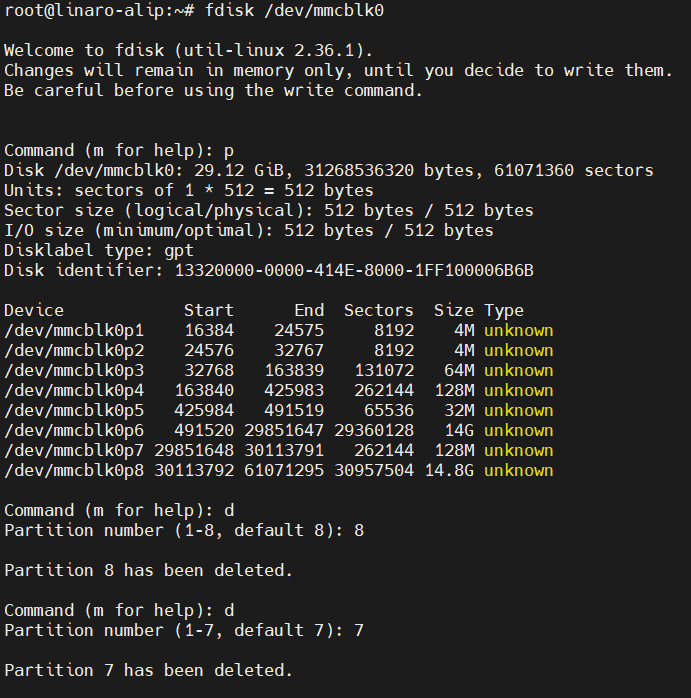
删除分区里输入wq命令
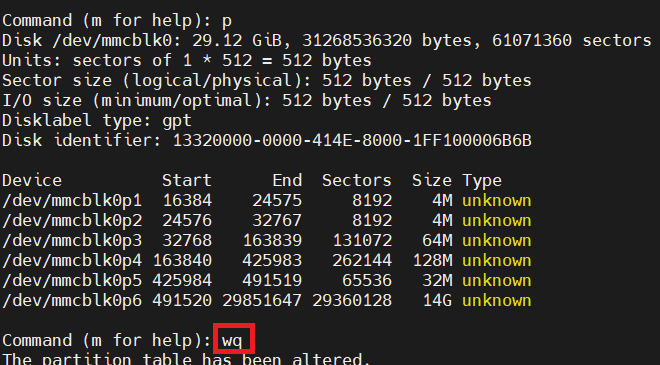
1.4.调整rootfs分区大小
parted /dev/mmcblk0
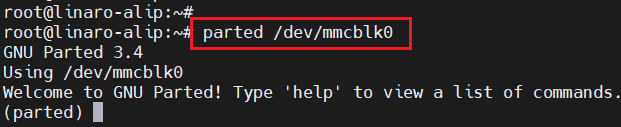
parted分区
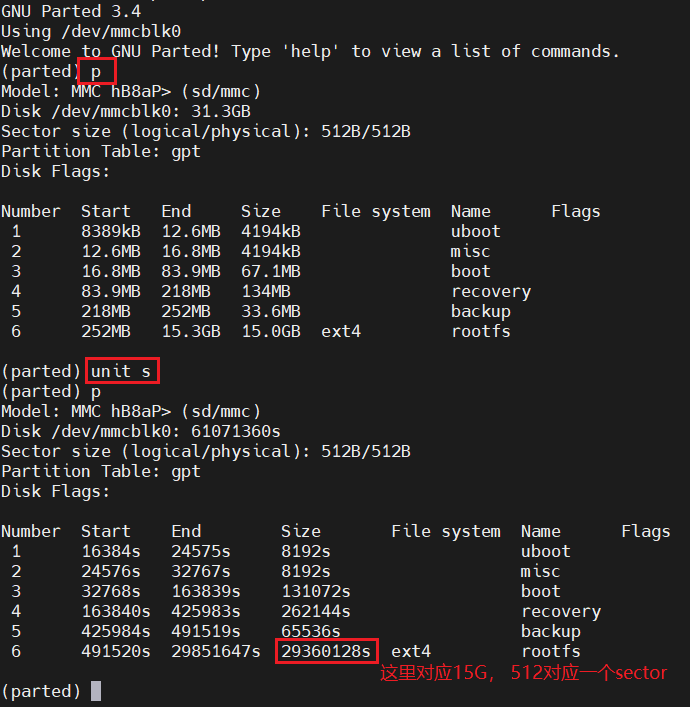
15G 对应的sector个数是29360128s
调整rootfs大小
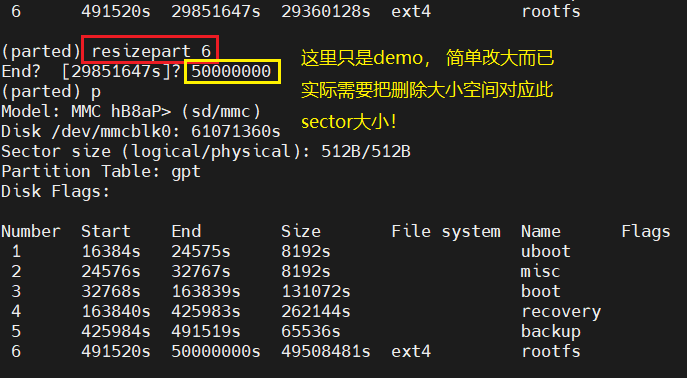
退出
1.5.使rootfs分区生效
resize2fs /dev/mmcblk0p6
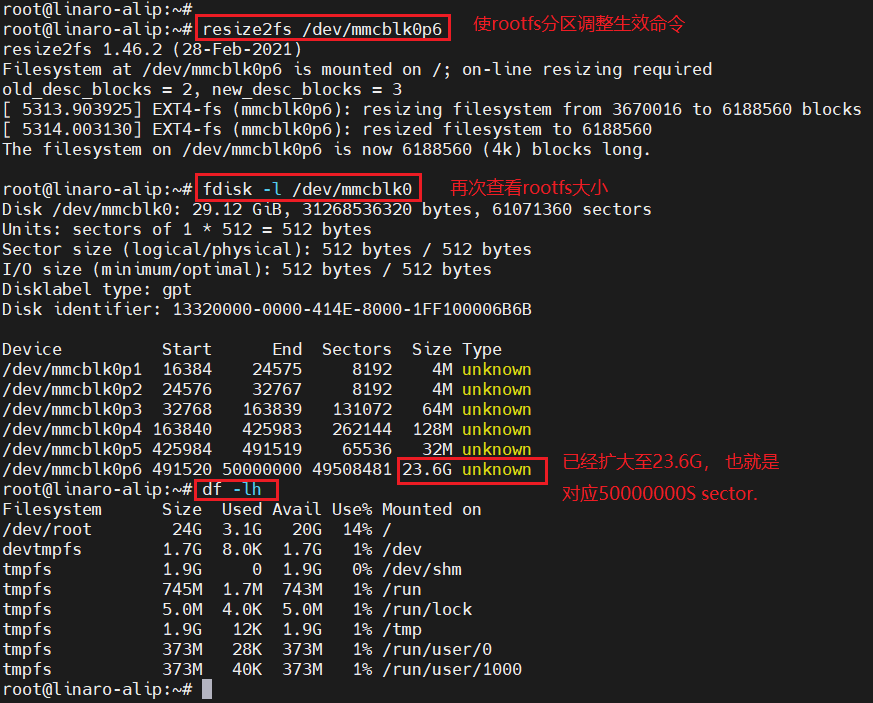
rootfs调整完成
2.buildroot中启用systemd
2.1.清除缓存
先清除之前编译buildroot所产生的缓存(注意:清除后再编译时间会较长), 如下命令:
2.2.选择配置
选择Neardi的开发板配置, 如下选择BoardConfig-rk3588-neardi-linux-lc160.mk

2.3.配置systemd
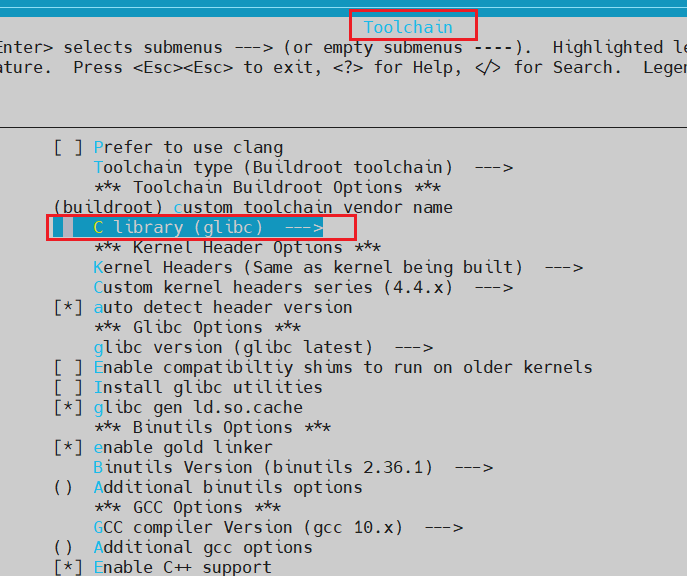
进入buildroot目录(cd buildroot), 执行ARCH=arm64 make menuconfig命令, 在ToolChain–>选择glibc,如下:
再选择System Configuration->Init system->systemd, 如下:
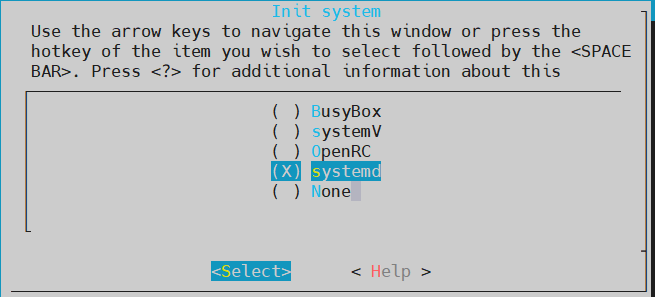
之后保存退出。
2.4.保存配置
ARCH=arm64 make savedefconfig
2.5.检查配置是否生效
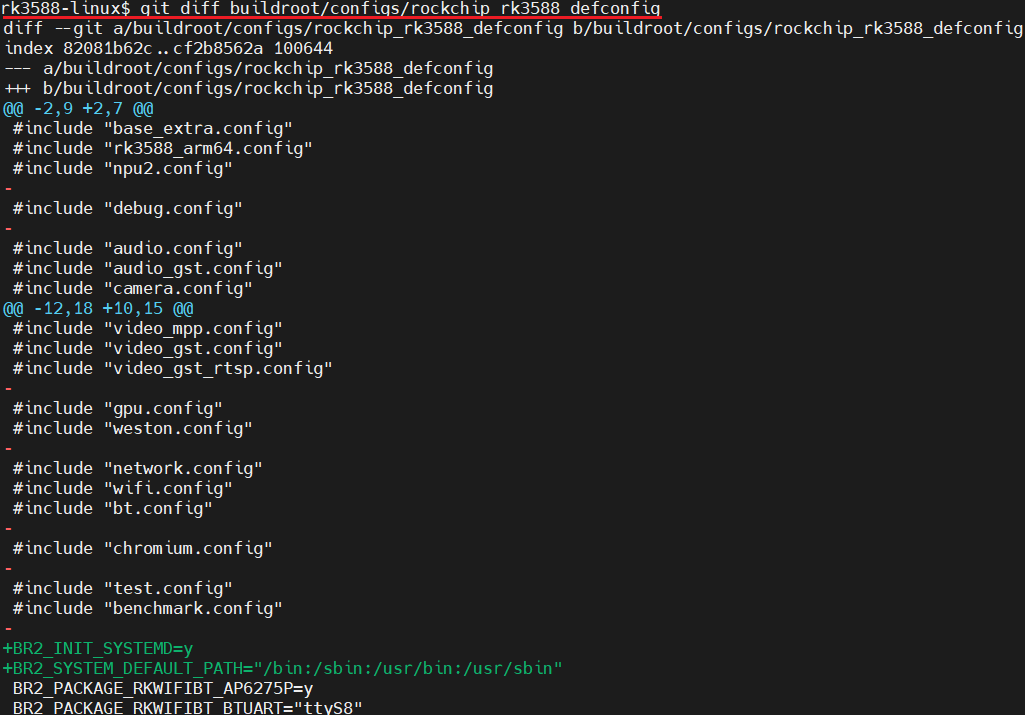
上图显示保存systemd至SDK配置文件中: buildroot/configs/rockchip_rk3588_defconfig
2.6.编译固件
./build.sh
编译成功后, 生成如下文件:
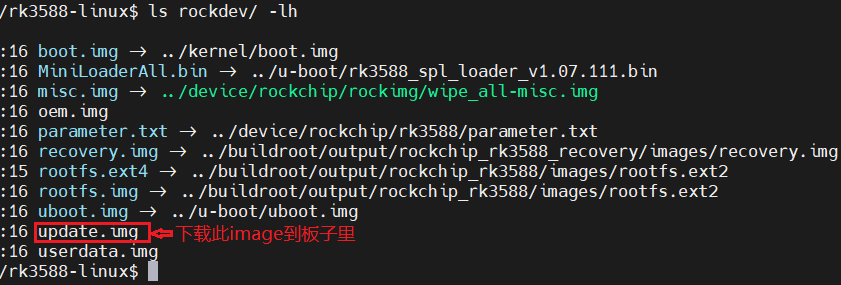
使用rockchip下载工具, 把update.img烧录到开发板。
2.7.验证systemd是否工作
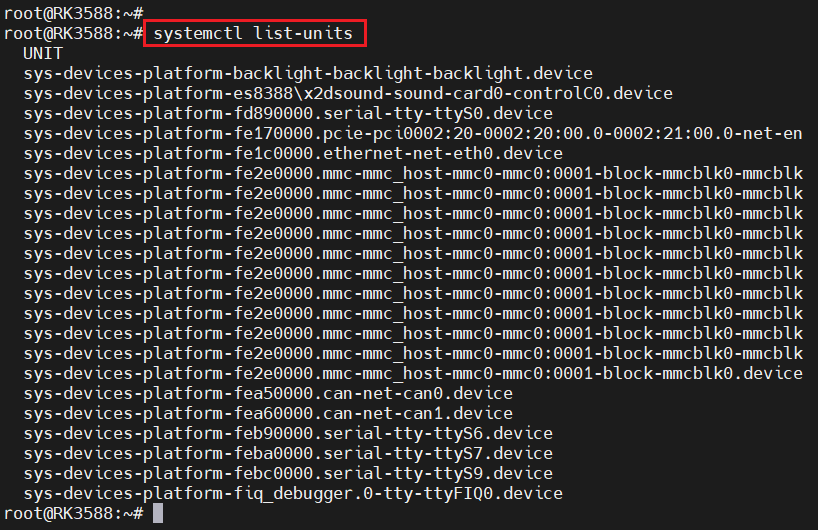
上图成功运行systemd。