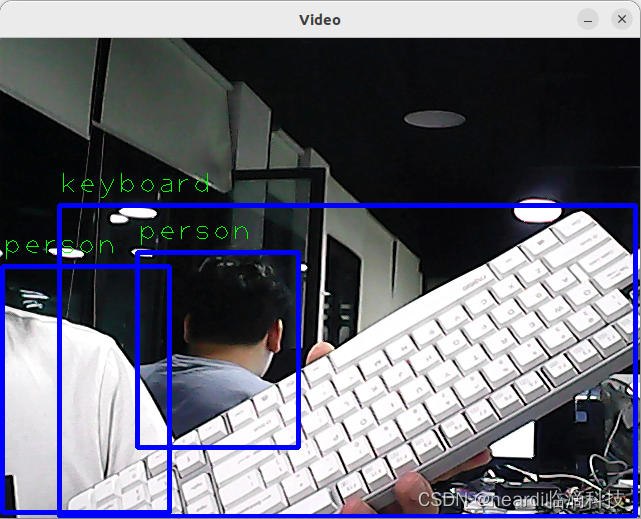
Real-Time Object Detection Using Camera
Environment Setup
Hardware: Neardi LPA3588 development board, USB camera (or other cameras)
Software: RK3588 SDK, Neardi LPA3588 Ubuntu image
Source Code Download
Download rknpu2 on the LPA3588 development board:
git clone https://github.com/rockchip-linux/rknpu2
OpenCV Installation
sudo apt install libopencv-dev libopencv-videoio-dev libopencv-video-dev libopencv-imgproc-dev libopencv-highgui-dev
Compilation
Navigate to the rknn_ssd_demo directory and modify CMakeLists.txt. The sample code uses OpenCV3 libraries, so we comment out to use the installed OpenCV4 library.
neardi@LPA3588:~/rknn/rknpu2/examples/rknn_ssd_demo$ git diff .
diff --git a/examples/rknn_ssd_demo/CMakeLists.txt b/examples/rknn_ssd_demo/CMakeLists.txt
index bd236f6..40537c1 100644
--- a/examples/rknn_ssd_demo/CMakeLists.txt
+++ b/examples/rknn_ssd_demo/CMakeLists.txt
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ else()
if(LIB_ARCH STREQUAL "armhf")
set(OpenCV_DIR ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/../3rdparty/opencv/opencv-linux-armhf/share/OpenCV)
else()
- set(OpenCV_DIR ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/../3rdparty/opencv/opencv-linux-aarch64/share/OpenCV)
+ #set(OpenCV_DIR ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/../3rdparty/opencv/opencv-linux-aarch64/share/OpenCV)
endif()
endif()
find_package(OpenCV REQUIRED)
The original rknn_ssd_demo analyzes images, hence single-threaded. Here, we modify it to perform object recognition from camera input, enhancing it with multi-threading. First, create a queue data structure (see attached queue.hpp).
Add new header files:
neardi@LPA3588:~/rknn/rknpu2/examples/rknn_ssd_demo$ git diff .
--- a/examples/rknn_ssd_demo/src/main.cc
+++ b/examples/rknn_ssd_demo/src/main.cc
@@ -29,6 +29,19 @@
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
+#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
+#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp"
+#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
+#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
+
+#include <opencv2/videoio/videoio.hpp>
+#include <opencv2/video.hpp>
+#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
+
+#include "rknn_api.h"
+#include "ssd.h"
+#include "queue.hpp"
+
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
Create two global variables, _idleimgbuf & _imgdata, to store images retrieved from the camera, with a maximum length of 300 pixels.
+/**
+ * create memory pool for images gotten from camera.
+ */
+Queue<cv::Mat*> _idleimgbuf;
+Queue<cv::Mat*> _imgdata;
+
Add thread functions to read data from the camera:
bool g_exit = false;
static int camera_thread(int index)
{
/**
* load image from camera
*/
cv::VideoCapture cap;
cap.open(index);
if (!cap.isOpened()) {
return -1;
}
cv::Mat first;
cap >> first;
for(int i = 0; i < max_img_count; i++) {
_idleimgbuf.push(new cv::Mat(first));
}
while (!g_exit)
{
cv::Mat* pimg = NULL;
_idleimgbuf.pop(pimg);
if (NULL != pimg) {
cap >> *pimg;
if (pimg->empty()) {
_idleimgbuf.push(pimg);
} else {
_idleimgbuf.push(pimg);
}
} else {
/**
* wait a moment to avoid consume high CPU performance.
*/
usleep(100);
continue;
}
}
cap.release();
return 0;
}
Here, we read the first frame from the camera to determine its frame size.
Modify input parameters and start thread code:
/*-------------------------------------------
Main Function
-------------------------------------------*/
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
const int img_width = 300;
const int img_height = 300;
const int img_channels = 3;
int ret = 0;
int model_len = 0;
unsigned char* model = nullptr;
rknn_context ctx = 0;
const char* model_path = argv[1];
if (argc != 3) {
printf("Usage:%s model camera\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
int index = std::stoi(argv[2]);
std::thread camthread(&camera_thread, index);
// Load RKNN Model
printf("Loading model ...\n");
model = load_model(model_path, &model_len);
...
return 0;
Change the main function to read data:
namedWindow("Video", 1);
do {
cv::Mat* pimg = nullptr;
_idleimgbuf.pop(pimg);
if (nullptr == pimg) {
usleep(100);
if (waitKey(30) >= 0) {
g_exit = true;
break;
}
continue;
}
// if origin model is from Caffe, you maybe not need do BGR2RGB.
cv::Mat orig_img = pimg->clone();
_idleimgbuf.push(pimg);
cv::Mat orig_img_rgb;
cv::cvtColor(orig_img, orig_img_rgb, cv::COLOR_BGR2RGB);
cv::Mat img = orig_img_rgb.clone();
if (orig_img_rgb.cols != img_width || orig_img_rgb.rows != img_height) {
printf("resize %d %d to %d %d\n", orig_img_rgb.cols, orig_img_rgb.rows, img_width, img_height);
cv::resize(orig_img_rgb, img, cv::Size(img_width, img_height), 0, 0, cv::INTER_LINEAR);
}
Release resources:
/**
* free the queue buffer.
*/
while(_idleimgbuf.size() > 0)
{
cv::Mat* pmat = NULL;
_idleimgbuf.pop(pmat);
if (NULL != pmat) {
delete pmat;
}
}
while(_imgdata.size() > 0)
{
cv::Mat* pmat = NULL;
_imgdata.pop(pmat);
if (NULL != pmat) {
delete pmat;
}
}
Compile and run rknn_ssd_demo:
./rknn_ssd_demo ./model/RK3588/ssd_inception_v2.rknn 41
Here, 41 refers to the index of /dev/video41 device. Adjust according to your camera input. Detection results are displayed as follows: